Introduction
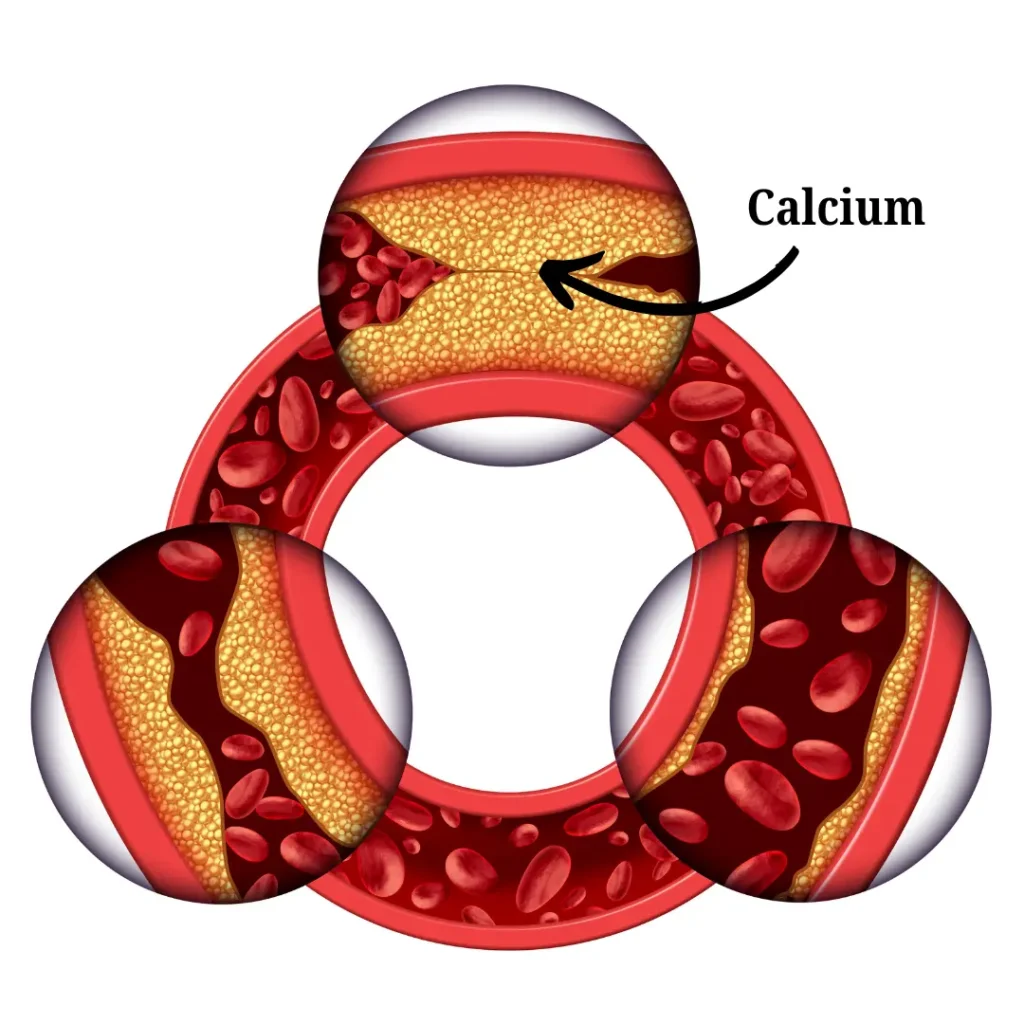
A calcium score test is a simple scan of the heart that helps doctors check for early signs of heart disease / coronary artery disease (CAD). It measures calcium buildup in the arteries, which can indicate a higher risk of heart problems like heart attacks. Calcium only starts to deposit after cholesterol has been accumulated in the arteries for some time. It is not the substance that causes the narrowing of the arteries but the one that causes hardening of the artery. When there is calcium detected in the arteries, it only tells the doctor that the arteries have cholesterol plaque present for some time. It does not determine the degree of narrowing of the arteries.
What is a Calcium Score?
The test gives a number called the calcium score, which shows how much calcium is in the arteries. The scores range from 0 to over 400:
- 0 : No calcium, very low risk of heart disease.
- 1 – 100 : Small amount of calcium, low to moderate risk.
- 101 – 300 : More calcium buildup, higher risk.
- 301 & above : A lot of calcium, very high risk of heart disease.
How is the Test Done?
The test is quick and painless. You will lie on a table while a special X-ray machine (CT machine) takes pictures of your heart. It takes about 10 -15 minutes and no needles or contrast dye are needed.
Who Should Get This Test?
This test is beneficial for people who may have a higher risk of heart disease but have not shown signs of symptoms yet. It may be recommended if:
- You are between 40 to 70 years of age with risk factors like smoking, high blood pressure.
- There is a family history of early heart disease.
- You have diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, or high cholesterol.
Why is the Calcium Score Test Helpful?
- Identifies early signs of CAD before symptoms show.
- Helps doctors understand your risk level and determine the necessity of lifestyle changes or medications.
- Assists in deciding whether interventions like statins or aspirin therapy are needed.
What Are the Downsides?
- It only detects hard calcium deposits, not soft plaques that can also lead to heart problems.
- It does not diagnose heart attacks or causes of chest pains.
- It uses a small amount of radiation, but the risk is low.
- It only tells the doctor that there is cholesterol build up in your arteries. It cannot show the degree of narrowing of the arteries.
Conclusion
Calcium scoring is an effective, non-invasive method for assessing the risk of CAD. While it’s not the only test doctors use, it provides crucial insights that can help with early intervention and preventive strategies for heart disease. If you have risk factors, talk to your doctor about whether this test is right for you.