Both the Treadmill Electrocardiogram (ECG) and the Stress Echocardiogram are types of cardiac stress tests designed to detect ischemia—a condition where reduced blood flow to the heart occurs due to severe or significant blockages in the coronary arteries.
Treadmill ECG
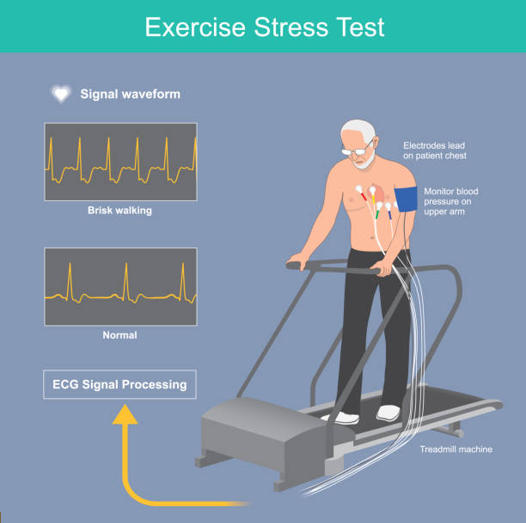
In a Treadmill ECG, patients are asked to walk or run on a treadmill while their heart’s electrical activity is monitored via ECG. This test aims to identify changes that suggest reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Accuracy: The sensitivity and specificity of this test are approximately 70%, meaning it correctly identifies ischemia about 70% of the time.
- Best use: It is considered a good initial screening tool, especially for patients with a low likelihood of coronary artery disease.
Stress Echocardiogram
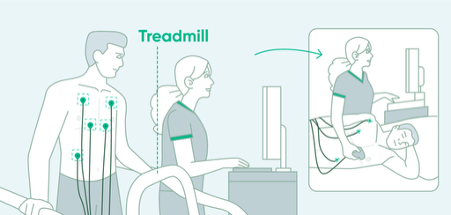
A Stress Echocardiogram combines a standard echocardiogram (ultrasound imaging of the heart) with a stress test.
- A baseline echocardiogram is performed first to evaluate the heart’s structure and function.
- If results are normal, the patient then undergoes a stress test. This can be done either by exercising on a treadmill or by receiving a medication called dobutamine, which simulates the effects of exercise for patients unable to walk or run.
- Immediately after stress, the echocardiogram is repeated to visually assess the heart for any signs of ischemia. ECG monitoring is also continued throughout the test.
- Accuracy: The sensitivity and specificity of the Stress Echocardiogram are around 85%, offering higher accuracy compared to the Treadmill ECG.
Summary
While the Treadmill ECG remains a valuable and accessible screening tool, particularly in patients with a lower risk of heart disease, the Stress Echocardiogram provides more detailed information—especially in selected patients—by evaluating heart structure, function and the presence of significant blockages. It is especially useful when structural heart assessment is also needed or when the patient is unable to exercise.
However, it is recommended to consult a Physician or Cardiologist to determine the most clinically appropriate diagnostic modality.
